Records Digitization Glossary
When we say “digitization,” what do we mean? Digitization is the process of converting a document from its original format (hard copy) into a digital version that can be processed by a computer. The original format could be paper, microfilm, photographs — any format that you can hold and see.
Fun fact: In researching the word “digitization,” it’s no surprise that the word saw a sharp increase in usage from the 1980s to present day (see Google trends chart below), as the internet grew and the demand for digital versions of records spiked.
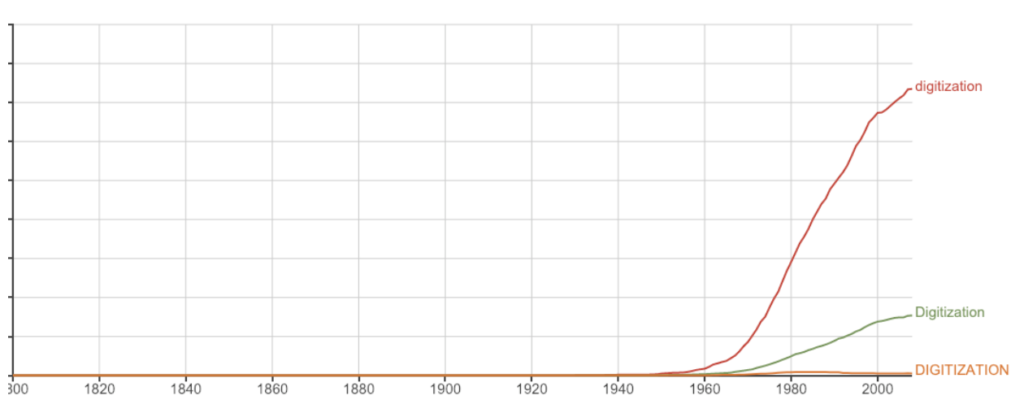
We’ve put together a list of common terms we use at BMI, and what we mean when we say them. If something is missing, let us know!
Access, Accessibility
When the term “access” is used in records digitization circles, it means the ability to find and use records. Not only does it mean having the tools to access information, but also having records organized and indexed in a way that makes them searchable.
Archival Agency, Institution
The archival agency, institution or organization is responsible for creating the archives. They determine the parameters for choosing records, acquiring them, converting them and making the actual archives available.
Archives
Records that are not current but have enduring value.
Attributes
Records are comprised of attributes, which are identifiers such as name, date, format or source.
Backup
Copying a file onto a second medium, such as a disk or tape, so the data is safe in case the original is corrupted.
Byte
Byte is a unit of measurement for digital files.
Cloud-Based Storage
This phrase is a little misleading. There’s not really a “cloud.” Your information is saved on a physical remote server that’s housed in a secure, protected facility. “Cloud” refers to the way you access the information, typically by logging in through a password-protected, secure website.
Conversion
In the digitization world, conversion refers to the act of changing a file or document from one format into another. For example, scanning documents and books from print form to digital files is a conversion.
Digital Preservation
Just like the phrase implies, digital preservation is the act of converting documents, files, books, videos, and other formats into a digital format so its useful life can be extended.
Digital ReeL
This is BMI’s trademarked digital preservation method of converting microfilm into a digital format that can be accessed from any computer, laptop or mobile device. Digital ReeL is a web-based solution.
Digitization
Conversion of analog materials, such as paper documents, into digital formats, such as PDFs, so they can be saved and accessed from any device, including laptops, computers, and smart devices.
Disaster Management and Recovery
Mitigating the risk of damage to your records. The best defense to losing records because of natural or man-made disaster is to have a disaster preparedness plan, which BMI can help you with.
Document Hosting
This term refers to where digital files are stored. Some organizations store files on servers onsite, while others use secure offsite storage. BMI offers storage on servers at our secure data center, which you can access through Digital ReeL.
Document Management System
A DMS tracks, manages and stores documents to reduce paper. They work with various file formats, and they’re more than just cloud-based storage systems. They can be automated to organize, index and store your records.
Electronic Document
Information that’s saved in a format that can be used by a computer or other device, such as a smartphone or tablet. An electronic document could be an email, text message, PDF, and any file format that’s transmitted digitally.
Field
A data field is the part of a database that’s designed to capture certain information, such as telephone numbers, author names, or serial numbers.
File
In our world, when we talk about files, we’re talking about the records that are comprised of sets of data, and they are organized in folders.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
A standard method used for transferring electronic files between a client and a network server.
Global Text Search
This refers to the way that users access digitally converted records. You enter a search term in the search box, and multiple tables or databases are searched.
HTML
Hypertext mark-up language is the type of code that’s used to build web pages.
Indexing
In digital records management, indexing refers to capturing meta information from records so that retrieval is easier.
Legacy Data, Legacy System
When we use the term “legacy” we are referring to records that still exist even though the technology may be outdated or the organization no longer uses the technology to access the records. Examples may be data stored on microfilm, CD ROM, floppy disks, or open-reel tapes.
Local-Area Network (LAN)
LAN is the network that links devices in a building or in a group of buildings, as in a university, hospital system or corporation.
Metadata
This is data that describes content of records. It’s data about data, and it’s like the fingerprint of the information.
Microfilm
What is microfilm? It’s an analog storage medium that stores documents on a length of film. BMI has been in the business of converting documents to microfilm for many years, and now we convert microfilm into Digital ReeL, a web-based format.
Migration
In the computer world, migration refers to moving records from one place to another. It could include conversion of the files from one format to another, but it includes moving the records from one storage location to another.
Open Format
A file format that isn’t proprietary, or files that are publicly available for anyone to access, use and transform.
Operational Records
These are also known as functional records because they’re used in the operations or running of an organization.
Preservation
The act of protected records from damage and deterioration. It’s also referred to as conservation.
Private Records
These are records that aren’t open or public. They can refer to personal records or any that are protected by privacy laws, especially in healthcare.
Records
A complete set of information in a database.
Scanning
BMI uses two scanning facilities. This is where physical conversion of your records takes place. Your paper, microfilm and other records are scanned and converted into text-searchable digital files.


